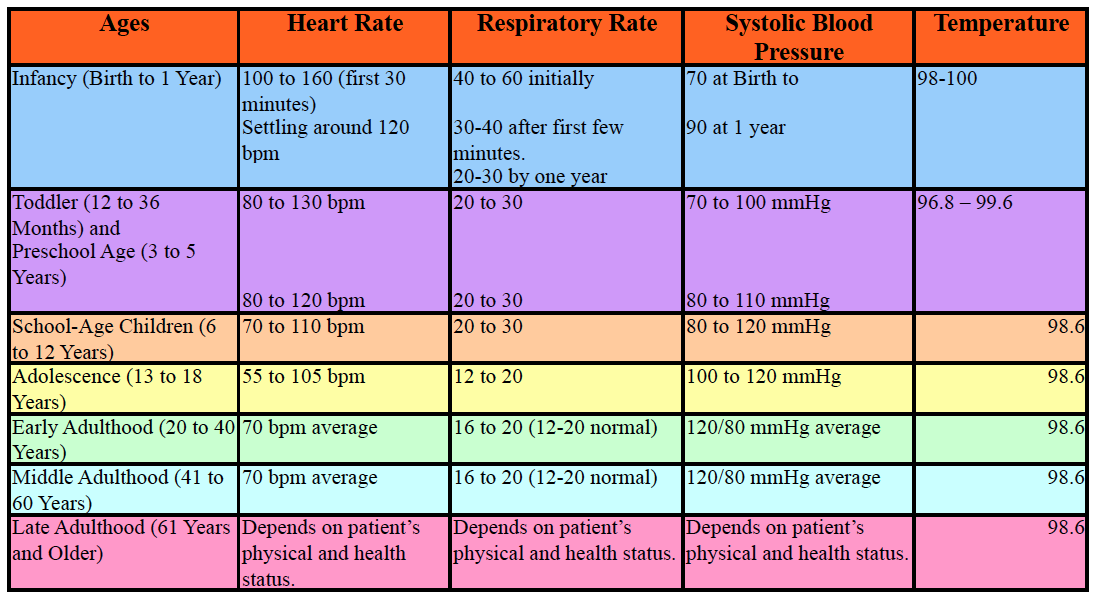
Vital Signs
Used to monitor vital body systems
They include...
- Temperature: Sites~oral, axillary, rectal, tympanic or temporal. Conditions~Hyperthermia, hypothermia, hypotension, frostbite, fever/pyrexia, febrile, heatstroke, heat exhaustion.
- Pulse: Sites~Temporal, Carotid, Apical, Brachial, Radial, Femoral, Popliteal, Posterior tibial and Dorsal Pedis. Rhythm~arrhythmia or dysrhythmia. Volume~ weak, thready, strong, bounding
- Respirations: Conditions~tachycardia, bradycardia, hypoxemia, hypercapnia, eupnea, tachypnea, bradypnea, hypoventilation, hyperventilation, apnea, dyspnea, orthopnea, pulse deficit
- Blood Pressure: Systolic and Diastolic. Conditions~ hypotension, hypertension, orthostatic hypotension,
- Pain: Pain scale 0-10
- Pulse Oximetry: Conditions~cyanosis
http://www.emt-national-training.com/vitals.php
Not only must a nurse know the normals and abnormals but also have the ability to critically think about these values. A nurse must read the lab values, vital signs and assess the patient appropriately.
1. Establish a Baseline.
2. Measure every 4-8 hrs. with a stable patient.
3. When there is a change in patient condition monitor more often and double check the vital signs.
4. If there is a change in patient condition the RN must monitor the vital signs and not delegate them to the UAP or the LVN.

No comments:
Post a Comment